Language/Multiple-languages/Vocabulary/Indo‐European-etymology
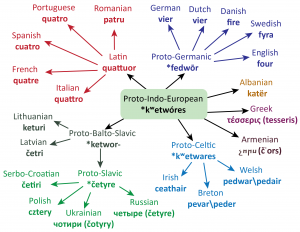
This is a page of the etymology of common words and morphemes in modern Indo-European languages.
In progress.
Proto-Albanian
Proto-Anatolian
Proto-Armenian
Proto-Balto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic
| etymon | derivative | etymon's cognate | etymon's Proto-Indo-European etymon |
|---|---|---|---|
Proto-Celtic
Proto-Greek
The Proto-Greek language (also known as Proto-Hellenic) was conventionally named the oldest form of the Greek language after its differentiation
from early Indo-European and before its division into more recent Greek dialects (Mycenaean, Doric, Attic-Ionian, Arcadian, Cypriot, Aeolian, etc.).
It is chronologically spoken approximately between the 30th and the 16th century BC.
Ancient Greek
| etymon | derivative | etymon's cognate | etymon's Proto-Indo-European etymon |
|---|---|---|---|
| ἔτυμος : true, real, genuine
ἔτυμος < ἔτεF-μος : (Ομήρ. Ὀδ. δ 140: ψεύσομαι ἦ ἔτυμον ἐρέω;) |
[ἐτυμολογία -etymology ]
(true meaning, etymological meaning of a word) |
ἐτεός < ἐτεF-ός
( probably cognate with verb"εἰμί") ἐτάζω, ἐξετάζω : examine, test, Ἐτεοκλῆς : Eteocles (truly glorious) |
ἐτεός and ἐτός
without reason, in vain, only with neg. οὐκ ἐτός :no wonder |
| *woikos-> (F)οῖκος , αλλά *wĺ̥kʷos > Λύκος (wolf) | |||
| mother (latin)
μητέρα (“metera” in greec) मातृ (“matar” in Sanskrit) |
|||
| pater (latin)
πατέρας ( pateras in Greek) vater (“fa-ter”) in German |
Proto-Italic
Latin
| etymon | derivative | etymon's cognate | etymon's Proto-Indo-European etymon |
|---|---|---|---|
Proto-Indo-Iranian
Proto-Iranian
| etymon | derivative | etymon's cognate | etymon's Proto-Indo-European etymon |
|---|---|---|---|
Proto-Indo-Aryan
Sanskrit
| etymon | derivative | etymon's cognate | etymon's Proto-Indo-European etymon |
|---|---|---|---|
Proto-Germanic
| etymon | derivative | etymon's cognate | etymon's Proto-Indo-European etymon |
|---|---|---|---|
| *ab | Danish: af
Dutch: af Elfdalian: åv English: of, off Faroese: av German: ab Icelandic: af Limburgish: aaf, aof Low German: af, of Luxembourgish: of Norwegian Bokmål: ab; av Plautdietsch: auf Scots: of, off, af, aff Saterfrisisch: oawe, ou Swedish: av, af Vlaams: of West Frisian: af, ôf Yiddish: אָפּ |
*h₂epó | |
| *an | Afrikaans: aan
Cimbrian: å Danish: å Dutch: aan Elfdalian: ą̊ English: on Faroese: á German: an Hunsrik: aan Icelandic: á Limburgish: aan Low German: an Luxembourgish: un North Frisian: a Norwegian: å Pennsylvania German: aa Saterfriesisch: an, oun Scots: an, on Swedish: å, a West Frisian: oan |
*h₂en- | |
| *andi | Afrikaans: en
Cimbrian: un Danish: end Dutch: en English: and Estonian: ent Faroese: enn Finnish: entä German: und Hunsrik: un Icelandic: enn Ingrian: entä Latvian: un Limburgish: ènde, ènd, èn, è Low German: un, on, en Luxembourgish: an Mócheno: ont North Frisian: en Norwegian: enn Pennsylvania German: un Plautdietsch: un, en Saterfrisisch: un Scots: an Swedish: än West Frisian: en, in Yiddish: און |
*h₂énti | |
| *at | Danish: at, ad
Elfdalian: að English: at Faroese: at Icelandic: að North Frisian: et, it, äät, äit Norwegian Bokmål: åt Scots: at Swedish: åt |
Latin: ad | *h₂éd |
| *beuną | English: be
Scots: be |
Latin: fuī, futūrus
Sanskrit: भवति |
*bʰuH- |
| *þat | Afrikaans: dat
Danish: det Dutch: dat, het English: that German: das, dass Faroese: tað, hað Icelandic: það Limburgish: det Low German: dat, datt Luxembourgish: dass; dat, datt Norwegian Bokmål: det Norwegian Nynorsk: det, dat Saterfriesisch: dat Scots: that Silesian: doas Swabian: des Swedish: det |
*só | |
| *þes- | Cimbrian: diiza
Dutch: deze, dit English: these German: diese Icelandic: þessi Limburgish: deze Low German: düsse, disse West Frisian: dizze |
*só | |
| *dōną | Afrikaans: doen
Bavarian: doa
Cimbrian: tüan, tüunan Dutch: doen English: do German: tun Hunsrik: dun Kölsch: dunn Limburgish: doon Low German: doon
Luxembourgish: doen, dinn, dunn North Frisian:
Pennsylvania German: duh Saterfriesisch: dwo Scots: dae Swabian: dua, doa West Frisian: dwaan Yiddish: טאָן |
*dʰeh₁- | |
| *ek, *ik | Afrikaans: ek
Bavarian: i Cimbrian: ich, i Danish: jeg, a, æ, ja, jæ Dutch: ik Elfdalian: ig English: ich; I Faroese: eg, jeg German: ich Hunsrik: ich Icelandic: ek, eg, ég Kölsch: ich Limburgish: ich, iech, ik Low German: ik Luxembourgish: ech Mócheno: i North Frisian: ick, ik Norwegian: ej, é, eig, í, æg, æj, æ, je, jæj
Pennsylvania German: ich Saterfriesisch: iek Scots: ik; A, I Silesian: iech Swabian: i Swedish: jag Upper Saxon: isch, ische West Frisian: ik Wymysorys: ych Yiddish: איך |
||
| *habjaną | Afrikaans: hê; hef
Cimbrian: haban, hen, håm; höoban Danish: have; hæve Dutch: hebben; heffen Elfdalian: åvå English: have; heave Faroese: hava; hevja German: haben; heben Hunsrik: hon Icelandic: hafa; hefja Kölsch: han Limburgish: höbbe; höffe Low German: heven
Luxembourgish: hunn; hiewen Mócheno: hom North Frisian:
Norwegian:
Pennsylvania German: hawwe Pfaelzisch: hann, hawwe, hunn Plautdietsch: haben Saterfriesisch: hääbe; hieuwje Scots: hae, ha, hiv, have, hawe; heave, heve, hewe Swabian: hau Swedish: ha, hava; häva Upper Saxon: ham, hom West Frisian: hawwe; heffe Westphalien:
Wymysorys: hon Yiddish: האָבן |
*keh₂p-, *kh₂pyéti | |
| *hit | Dutch: het
English: it, hit Limburgish: hèt Low German: et, it Plautdietsch: et Saterfriesisch: et Scots: it West Frisian: it |
*ḱe(y)- | |
| *hiz | Dutch: hij, ie
English: he Limburgish: hae Low German: he Luxembourgish: hien North Frisian: hi, he
Saterfriesisch: hie Scots: he West Frisian: hy Wymysorys: hār |
*ḱe + *ís | |
| *in | Afrikaans: in
Bavarian: i Cimbrian: inn, in Danish: i Dutch: in Elfdalian: i English: in Faroese: í, íggj German: in Icelandic: í Limburgish: in Luxembourgish: an Norwegian: i Pennsylvania German: in Pfaelzisch: in, en Saterfriesisch: in Scots: in Swedish: i West Frisian: yn Yiddish: אין |
*h₁én | |
| *izwiz | Afrikaans: jou
Cimbrian: òich Dutch: u; jou, a English: you German: euch Icelandic: yður Low German: ju, jug, jo, jau, u, ugg Luxembourgish: iech North Frisian: juu Norwegian Bokmål: dere Norwegian Nynorsk: øder Saterfriesisch: jou, Jou Scots: you Swedish: eder, er West Frisian: jo |
*yū́ | |
| *ne, *ni | Dutch: n-
English: ne German: nee Icelandic: né Scots: ne |
*ne | |
| *sa | Afrikaans: die
Bavarian: da Cimbrian: dèar, dar Dutch: de English: the German: der Faroese: sá Hunsrik: dää Icelandic: sá Kölsch: dä Limburgish: dae Low German: de Mócheno: der Saterfrisisch: die Scots: the Swabian: d'r Swedish: de West Frisian: de, dy Yiddish: דער |
Ancient Greek: ὁ
Sanskrit: स Tocharian B: se |
*só |
| *ta | Afrikaans: te, tot
Dutch: te, tot German: zu |
*do | |
| *tō | Afrikaans: tot; toe
Cimbrian: zo Dutch: toe; tot English: to, too German: zu Limburgish: tót Low German: to Luxembourgish: zou, zu North Frisian: to, tö, tu Saterfrisisch: tou Scots: tae West Frisian: ta Wymysorys: cy Yiddish: צו |
*doh₁ | |
| *wiþrą | Dutch: weder, weer
English: wither German: wider, wieder Hunsrik: witter Low German: wedder Swedish: vid, veder- |
*wi + *-teros | |
| *wihtiz | Danish: vætte
Dutch: wicht English: wight, whit; weight German: Wicht Faroese: vættur, veittur Icelandic: vættur Low German:
North Frisian: wecht Norwegian: vette, vætte, vett, vitt Saterfrisisch: nit; Wächte Scots: wicht; wecht, weicht Swedish: vätte Westphalien:
|
Proto-Slavic: *veťь | *wekti- |