Difference between revisions of "Language/Modern-greek-1453/Grammar/Moods"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:2de2bb59e24d48f4ee243181148844cd.jpg|thumb]] | [[File:2de2bb59e24d48f4ee243181148844cd.jpg|thumb]] | ||
<div class="pg_page_title">The 3 moods in Modern Greek</div> | <div class="pg_page_title">The 3 moods in Modern Greek</div> | ||
The citation form of a Greek verb is represented by the 1st person singular in the simple present tense. | |||
Certain verbs indicate an action occurring in the present: | |||
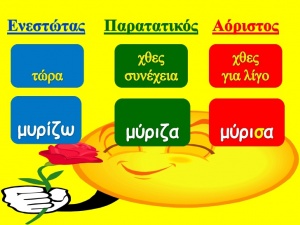
εγώ ποτίζω τώρα τα λουλούδια: I am watering the flowers now. | |||
Applying linguistic principles across various languages, grammar can differ significantly. | |||
The analysis of the Greek language leads to the introduction of new terms. Some verbs represent actions happening in the present: | |||
εγώ ποτίζω τώρα τα λουλούδια: I am watering the flowers now. | |||
Other verbs describe actions that took place in the past: | |||
Other verbs in the | |||
Χθες πότισα τα λουλούδια: Yesterday, I watered the flowers. | Χθες πότισα τα λουλούδια: Yesterday, I watered the flowers. | ||
And | And some verbs express actions that will occur in the future: | ||
Αύριο εγώ θα ποτίσω τα λουλούδια: Tomorrow, I will water the flowers. | Αύριο εγώ θα ποτίσω τα λουλούδια: Tomorrow, I will water the flowers. | ||
This is why | This is why there are 8 verb tenses, which can refer to actions happening in the present, the past, or the future. | ||
We | We categorize time in three stages: past, present, and future. | ||
Greek has eight verbal tenses (excluding imperative, participle, subjunctive, etc.): | |||
To | To understand the types of actions and their usage, refer to the following tables: | ||
=== | ==Present Tenses== | ||
===Ενεστώτας=== | |||
The present tense generally describes an action, event, or condition occurring in the present. | |||
Όλο το πρωί καθαρίζω το σπίτι. (τώρα-συνέχεια) | Όλο το πρωί καθαρίζω το σπίτι. (τώρα-συνέχεια) | ||
Every morning I clean the house | Every morning, I clean the house. | ||
The | ===Παρακείμενος=== | ||
The present perfect tense connects the past with the present, expressing a completed action in the past with consequences that extend to the present. | |||
Τώρα που ήρθες, έχω καθαρίσει ήδη το σπίτι. (έχει τελειώσει τώρα) | Τώρα που ήρθες, έχω καθαρίσει ήδη το σπίτι. (έχει τελειώσει τώρα) | ||
Now that you've | Now that you've arrived, I've already cleaned the house. | ||
=== | ==Future Tenses== | ||
===εξακολουθητικός μέλλοντας=== | |||
The future continuous tense expresses the duration or repetition of actions in the future. | |||
Όλο το πρωί θα καθαρίζω το σπίτι. | Όλο το πρωί θα καθαρίζω το σπίτι. | ||
All morning I will | All morning, I will be cleaning the house. | ||
===στιγμιαίος μέλλοντας=== | |||
The simple future tense describes an action or event that will occur in the future without specifying its duration. | |||
Αύριο το πρωί θα καθαρίσω το σπίτι. (μέλλον-κάποια στιγμή) | Αύριο το πρωί θα καθαρίσω το σπίτι. (μέλλον-κάποια στιγμή) | ||
Tomorrow morning I | Tomorrow morning, I will clean the house. | ||
===συντελεσμένος μέλλοντας=== | |||
The future perfect tense refers to a future action or event, showing that the action or event described by the verb will be completed in the future before another action, event, or specific point in time. | |||
be completed in the future before another action, event or | |||
Όταν θα έρθεις, εγώ θα έχω καθαρίσει το σπίτι. | Όταν θα έρθεις, εγώ θα έχω καθαρίσει το σπίτι. | ||
When you | When you arrive, I will have cleaned the house. | ||
=== | == Past Tenses== | ||
===Παρατατικός=== | |||
The imperfect tense expresses duration and repetition in the past, and is used to indicate a habitual action or event that occurred in the past. | |||
χτες όλο το πρωί καθάριζα το σπίτι | χτες όλο το πρωί καθάριζα το σπίτι | ||
Yesterday, I was cleaning the house all morning. | |||
===Αόριστος=== | |||
The simple past tense is used to describe an action, event, or condition that took place in the past. The action or event described was completed at some point. | |||
Χτες το πρωί καθάρισα το σπίτι. | Χτες το πρωί καθάρισα το σπίτι. | ||
Yesterday, I cleaned the house. | |||
===υπερσυντέλικος=== | |||
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action or event that occurred in the past, showing that the action described by the verb was completed before another past action or a specific point in time. | |||
Όταν ήρθες, εγώ είχα καθαρίσει το σπίτι. | |||
By the time you arrived, I had cleaned the house. | |||
==Summary== | |||
In summary, Greek verbs have eight tenses that describe actions, events, or conditions in the past, present, or future. Understanding the distinctions between these tenses is crucial for effective communication in the Greek language. Each tense serves a specific purpose and provides context to a sentence, allowing the speaker or listener to accurately interpret the timing of events. | |||
It is important to note that in addition to the eight tenses mentioned, Greek also has other verb forms and moods, such as the imperative, participle, and subjunctive, which are used in different grammatical contexts to convey various nuances of meaning. | |||
To master the Greek language, it is essential to practice using these tenses in various contexts and to familiarize oneself with the conjugation patterns of Greek verbs. By doing so, one can effectively communicate ideas, emotions, and intentions in the Greek language, and develop a deeper understanding of the rich linguistic and cultural heritage associated with it. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 22:19, 26 March 2023
The citation form of a Greek verb is represented by the 1st person singular in the simple present tense.
Certain verbs indicate an action occurring in the present:
εγώ ποτίζω τώρα τα λουλούδια: I am watering the flowers now.
Applying linguistic principles across various languages, grammar can differ significantly.
The analysis of the Greek language leads to the introduction of new terms. Some verbs represent actions happening in the present:
εγώ ποτίζω τώρα τα λουλούδια: I am watering the flowers now.
Other verbs describe actions that took place in the past:
Χθες πότισα τα λουλούδια: Yesterday, I watered the flowers.
And some verbs express actions that will occur in the future:
Αύριο εγώ θα ποτίσω τα λουλούδια: Tomorrow, I will water the flowers.
This is why there are 8 verb tenses, which can refer to actions happening in the present, the past, or the future.
We categorize time in three stages: past, present, and future.
Greek has eight verbal tenses (excluding imperative, participle, subjunctive, etc.):
To understand the types of actions and their usage, refer to the following tables:
Present Tenses
Ενεστώτας
The present tense generally describes an action, event, or condition occurring in the present.
Όλο το πρωί καθαρίζω το σπίτι. (τώρα-συνέχεια)
Every morning, I clean the house.
Παρακείμενος
The present perfect tense connects the past with the present, expressing a completed action in the past with consequences that extend to the present.
Τώρα που ήρθες, έχω καθαρίσει ήδη το σπίτι. (έχει τελειώσει τώρα)
Now that you've arrived, I've already cleaned the house.
Future Tenses
εξακολουθητικός μέλλοντας
The future continuous tense expresses the duration or repetition of actions in the future.
Όλο το πρωί θα καθαρίζω το σπίτι.
All morning, I will be cleaning the house.
στιγμιαίος μέλλοντας
The simple future tense describes an action or event that will occur in the future without specifying its duration.
Αύριο το πρωί θα καθαρίσω το σπίτι. (μέλλον-κάποια στιγμή)
Tomorrow morning, I will clean the house.
συντελεσμένος μέλλοντας
The future perfect tense refers to a future action or event, showing that the action or event described by the verb will be completed in the future before another action, event, or specific point in time.
Όταν θα έρθεις, εγώ θα έχω καθαρίσει το σπίτι.
When you arrive, I will have cleaned the house.
Past Tenses
Παρατατικός
The imperfect tense expresses duration and repetition in the past, and is used to indicate a habitual action or event that occurred in the past.
χτες όλο το πρωί καθάριζα το σπίτι
Yesterday, I was cleaning the house all morning.
Αόριστος
The simple past tense is used to describe an action, event, or condition that took place in the past. The action or event described was completed at some point.
Χτες το πρωί καθάρισα το σπίτι.
Yesterday, I cleaned the house.
υπερσυντέλικος
The past perfect tense is used to describe an action or event that occurred in the past, showing that the action described by the verb was completed before another past action or a specific point in time.
Όταν ήρθες, εγώ είχα καθαρίσει το σπίτι.
By the time you arrived, I had cleaned the house.
Summary
In summary, Greek verbs have eight tenses that describe actions, events, or conditions in the past, present, or future. Understanding the distinctions between these tenses is crucial for effective communication in the Greek language. Each tense serves a specific purpose and provides context to a sentence, allowing the speaker or listener to accurately interpret the timing of events.
It is important to note that in addition to the eight tenses mentioned, Greek also has other verb forms and moods, such as the imperative, participle, and subjunctive, which are used in different grammatical contexts to convey various nuances of meaning.
To master the Greek language, it is essential to practice using these tenses in various contexts and to familiarize oneself with the conjugation patterns of Greek verbs. By doing so, one can effectively communicate ideas, emotions, and intentions in the Greek language, and develop a deeper understanding of the rich linguistic and cultural heritage associated with it.
| The indicative - «οριστική» | The subjunctive - «υποτακτική» | The imperative «προστακτική» | The participle « μετοχή » |
| This mood represents reality and it is used to give information about a situation, an operation or event. A negation is formed with the particle «δεν» which preceded the verb.
Eg: 1. Πηγαίνω στο σχολείο : I go to school 2. Ο Γιάννης δεν γύρισε ακόμα : John did not return yet |
The subjunctive mood denotes an expression of will. When we are influenced by something, are afraid of something, desire, suggest, propose, recommend, wish, fear, allow, admit, imply something, the subjunctive is used. This mood is formed by the usage of the particles «να» and «ας» and a verb-form. In negative utterances the particle «μην» is put between «να» or «ας» and the verb-form.
Eg : 1. Θέλω να παίξουμε I want that we play 2. Δέν μπορώ νά μήν πάω! I can't not go |
This mood is used to give orders or instructions by asking, demanding or requiring people to do things. For negative expressions the subjunctive is employed, because the imperative cannot be negated.
Eg : 1. Βγες έξω! : Go away! 2. (Να) μη φορέσεις αυτό το παντελόνι! Don't wear that trousers! |
a)shows us how the verb is described, like the adverbial participle
Eg : Οι κληρωμένοι λαχνοί ανακοινώθηκαν The drawn lottery tickets were announced b) gives a property to a noun, like an adjective, here for the explanation Thus, the participle could be both a form of the verb and an adjective, moreover the word participle also means that it consists of two forms. The inflections of the Modern Greek adjectives derived from active and passive participles and some participles from Ancient Greek verbs. Eg : 1.Δε θέλω να τα δω ανακατωμένα, όπως την προηγούμεναi φορά. : I don't want it to be seen mixed, like the previous time 2. Σήμερα ήμουν πολύ αγχωμένος στο σχολείο. Today I was very stressed in school |
The infinitive « απαρέμφατο »
The infinitive in the Greek language is an intransitive verbal form which means: what does not reveal the face of its subject.
The infinitive in modern Greek is not used alone, but with the auxiliary verb "to have" for the formation of completed verbal tenses:
eg :
έχει λύσει :
it has solved
έχει γράψει :
it has written
έχει λυθεί :
it has been solved . |- |
Summary of All Tenses
| Παρελθοντικοί :
Grammatical tenses of past |
Παροντικοί :
Nature of the activity |
Μελλοντικοί : indicative mood « future » |
| Παρατατικός :
Past Continuous / imparfait |
Ενεστώτας : simple present / présent | εξακολουθητικός μέλλοντας :
future continuous / futur |
| Αόριστος :
simple past / passé simple |
Παρακείμενος :
present perfect / passé composé |
στιγμιαίος μέλλοντας : simple future / futur proche |
| Υπερσυντέλικος :
past perfect / Plus-que-parfait
|
|
συντελεσμένος μέλλοντας :
future perfect / futur antérieur
|