Difference between revisions of "Language/French/Grammar/Degree-adverbs"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Quick edit) |
m (Quick edit) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:French-Language-PolyglotClub.png|thumb]] | [[File:French-Language-PolyglotClub.png|thumb]] | ||
<div | <div class="pg_page_title"> Degree adverbs</div> | ||
==What are Degree Adverbs?== | ==What are Degree Adverbs?== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
*Je fume modérément | *Je fume modérément | ||
I smoke moderately | I smoke moderately | ||
*Tout est si clair maintenant | *Tout est si clair maintenant | ||
Everything is so clear | Everything is so clear | ||
*Ce ne sera pas tout à fait la vérité | *Ce ne sera pas tout à fait la vérité | ||
That won't be entirely the truth | That won't be entirely the truth | ||
*Je tends ma main jusqu'à presque toucher son visage | *Je tends ma main jusqu'à presque toucher son visage | ||
I stretch out my hand almost to touch his face | I stretch out my hand almost to touch his face | ||
*Elle a dressé trop brusquement la tête | *Elle a dressé trop brusquement la tête | ||
She lifted her head up too quickly | She lifted her head up too quickly | ||
==TABLE Typical degree adverbs== | ==TABLE Typical degree adverbs== | ||
| Line 79: | Line 74: | ||
|She talks too much | |She talks too much | ||
|} | |} | ||
A number of degree adverbs also function as quantifiers modifying nouns : | A number of degree adverbs also function as quantifiers modifying nouns : | ||
| Line 109: | Line 101: | ||
===French Lesson 100 - Adverbs of Quantity Intensity Degree - YouTube=== | ===French Lesson 100 - Adverbs of Quantity Intensity Degree - YouTube=== | ||
<youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTjAjr5IL3s</youtube> | <youtube>https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTjAjr5IL3s</youtube> | ||
==Other Lessons== | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Should-I-say-"Madame-le-juge"-or-"Madame-la-juge"?|Should I say "Madame le juge" or "Madame la juge"?]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Present-Tense|Present Tense]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Adverbs|Adverbs]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Gender-of-Nouns-Names-of-ships-and-restaurants|Gender of Nouns Names of ships and restaurants]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/How-to-use-Have|How to use Have]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Definite-and-indefinite-articles|Definite and indefinite articles]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Plurals|Plurals]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Adjectives-which-regularly-occur-before-and-after-the-noun,-but-with-a-change-of-meaning|Adjectives which regularly occur before and after the noun, but with a change of meaning]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Agreement-of-past-participles-with-preceding-direct-objects-in-questions|Agreement of past participles with preceding direct objects in questions]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/“être”-and-“avoir”-with-verbs-used-intransitively-and-transitively|“être” and “avoir” with verbs used intransitively and transitively]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Pronouns-referring-to-groups-of-mixed-gender|Pronouns referring to groups of mixed gender]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Dates|Dates]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Nouns-which-have-the-same-spoken-form-but-two-different-written-forms|Nouns which have the same spoken form but two different written forms]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Homophones|Homophones]] | |||
* [[Language/French/Grammar/Adjectifs-possessifs|Adjectifs possessifs]] | |||
<span links></span> | |||
Latest revision as of 13:56, 27 March 2023
Degree adverbs
What are Degree Adverbs?[edit | edit source]
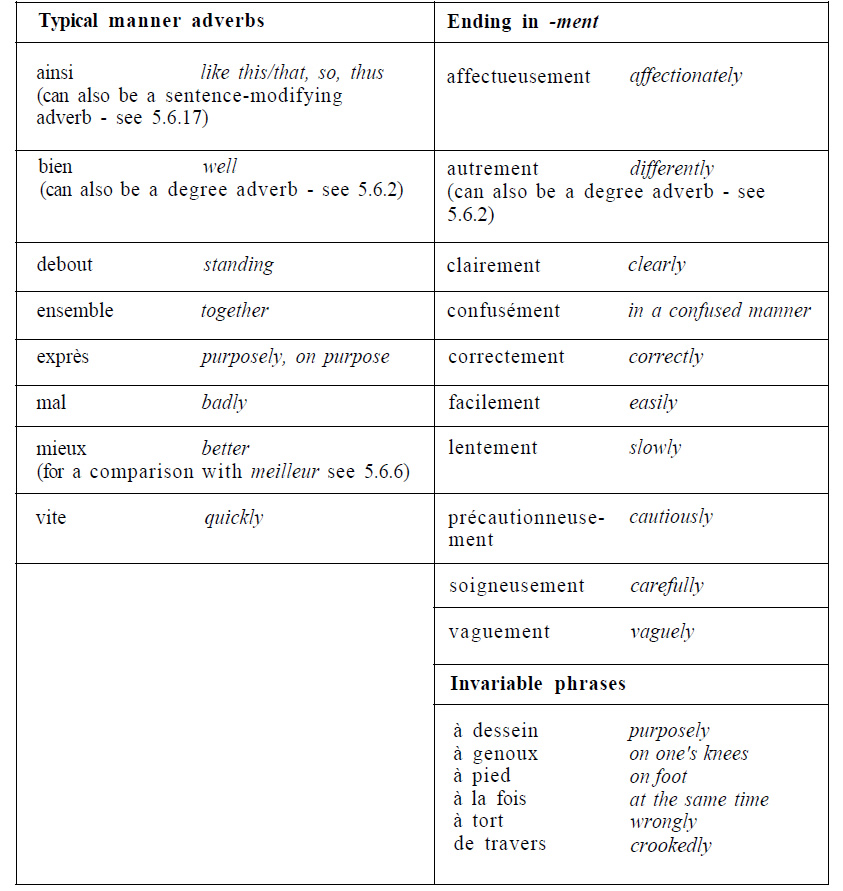
Adverbs which indicate the extent to which something is the case are degree adverbs. As a class they can modify every kind of sentence element: verbs, adjectives, nouns, prepositions and other adverbs. But individually some of them may be restricted to modifying particular categories of item (e.g. très can modify adjectives, prepositions and adverbs - très heureux 'very happy', très à la mode 'very fashionable', très bien 'very well' - but not verbs *Je fume très 'I smoke very'):
Examples[edit | edit source]
- Je fume modérément
I smoke moderately
- Tout est si clair maintenant
Everything is so clear
- Ce ne sera pas tout à fait la vérité
That won't be entirely the truth
- Je tends ma main jusqu'à presque toucher son visage
I stretch out my hand almost to touch his face
- Elle a dressé trop brusquement la tête
She lifted her head up too quickly
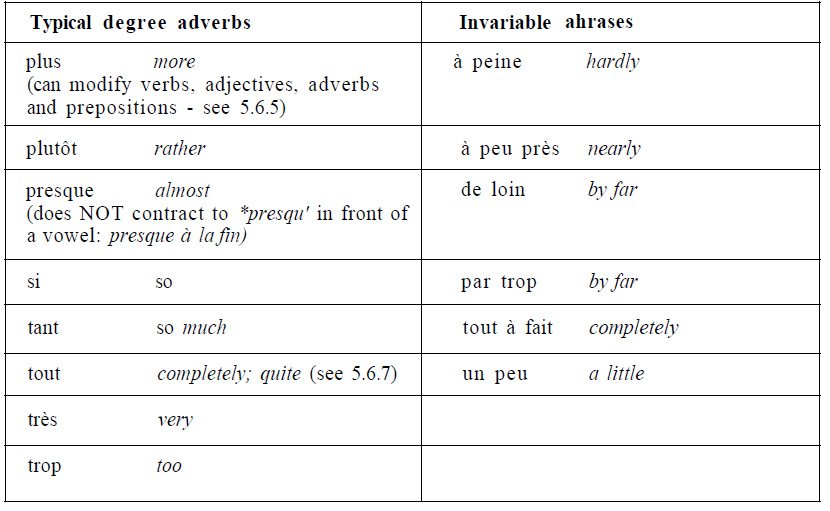
TABLE Typical degree adverbs[edit | edit source]
Representative examples[edit | edit source]
| French | English |
|---|---|
| C'est un acteur assez connu | He is quite a well-known actor |
| La route tue autant que la guerre | Road accidents are the cause of as many deaths as war |
| Elle est autrement intelligente que sa soeur | She is much more intelligent than her sister |
| Ils ont beaucoup discuté pendant le weekend | They spent a lot of time discussing over the weekend |
| C'est bien bête | That's really stupid |
| Il y en a davantage qu'on ne le pense | There are more than you think |
| Elle a acheté un billet juste avant de prendre le train | She bought a ticket just before catching the train |
| On ramène même des souvenirs | They even bring back souvenirs |
| Voici le vélo même dont il s'est servi | This is the very bike he used |
| un monde si étrangement silencieux | such a strangely silent world |
| Elle est tellement plus sympathique | She is so much nicer |
| J'ai répondu tout de travers | 1 replied in a quite confused way |
| Je suis ici depuis très longtemps | I have been here for a very long time |
| Elle parle trop | She talks too much |
A number of degree adverbs also function as quantifiers modifying nouns :
| French | English |
|---|---|
| assez d'excuses | enough excuses |
| autant d'argent | as much money |
| beaucoup de clients | many customers |
| bien des problèmes | many problems |
| tellement de travail | so much work |
Videos[edit | edit source]
French Lesson 100 - Adverbs of Quantity Intensity Degree - YouTube[edit | edit source]
Other Lessons[edit | edit source]
- Should I say "Madame le juge" or "Madame la juge"?
- Present Tense
- Adverbs
- Gender of Nouns Names of ships and restaurants
- How to use Have
- Definite and indefinite articles
- Plurals
- Adjectives which regularly occur before and after the noun, but with a change of meaning
- Agreement of past participles with preceding direct objects in questions
- “être” and “avoir” with verbs used intransitively and transitively
- Pronouns referring to groups of mixed gender
- Dates
- Nouns which have the same spoken form but two different written forms
- Homophones
- Adjectifs possessifs