Language/Multiple-languages/Culture/Introduction-to-Writing-Systems
Writing systems are visual carriers of languages. They are tools, so they can be evaluated as tools. Here are the important information about them.
In progress.
Logogram
It is the earliest form of writing systems. As what its name suggests, they are pictures (logo).
At this stage, the direction of text is various, even being zigzag in Mayan and others.
Its advantage is able to express the meaning easily, even without needing unified pronunciations. Its disadvantage is having too many glyphs to memorise.
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatolian | Luwian | Anatolia | 14th to 13th century BC – 7th century BC | 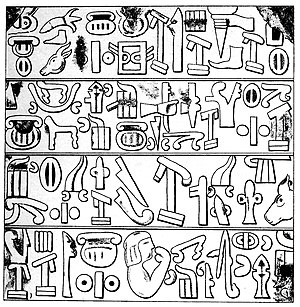
| |
| Aztec | Nahuatl | Mesoamerica | ? – c. 1530 | 
| |
| Chữ Nôm | Vietnamese | Vietnam | 15th century – 19th century | Han | 
|
| Cretan | Minoan | Crete | c. 2100 BC – 1700 BC | 
(Δίσκος της Φαιστού Dískos tis Phaistós) | |
| Cuneiform | Sumerian, Akkadian, etc. | Mesopotamia | c. 35th century BC – 2nd century | 
| |
| Cypro-Minoan | Eteocypriot | Cyprus | c. 1550 BC – 1050 BC | Linear A | 
|
| Dongba | Naxi | Southeastern China | 1000 – | 
| |
| Egyptian | Egyptian | Egypt | c. 3200 BC – 400 | 
| |
| Han | Chinese, etc. | East Asia | 2nd millennium BC – | 
| |
| Jurchen | Jurchen | Northeastern China | 12th century–16th century | Han | 
|
| Khitan large script | Khitan | Northeast Asia | 920 – 1191 | Han | 
|
| Linear A | Minoan | Crete | c. 1800 BC – 1450 BC | 
| |
| Mayan | Chʼoltiʼ, Yucatec Maya, etc. | Mesoamerica | 3rd century BC – 16th century | 
| |
| Mixtec | Mixtec languages | Mesoamerica | ? – c. 1530 | 
| |
| Sawndip | Zhuang | Southern China | 7th century – | Han | 
|
| Sui | Sui | Southern China | ? – | Han | 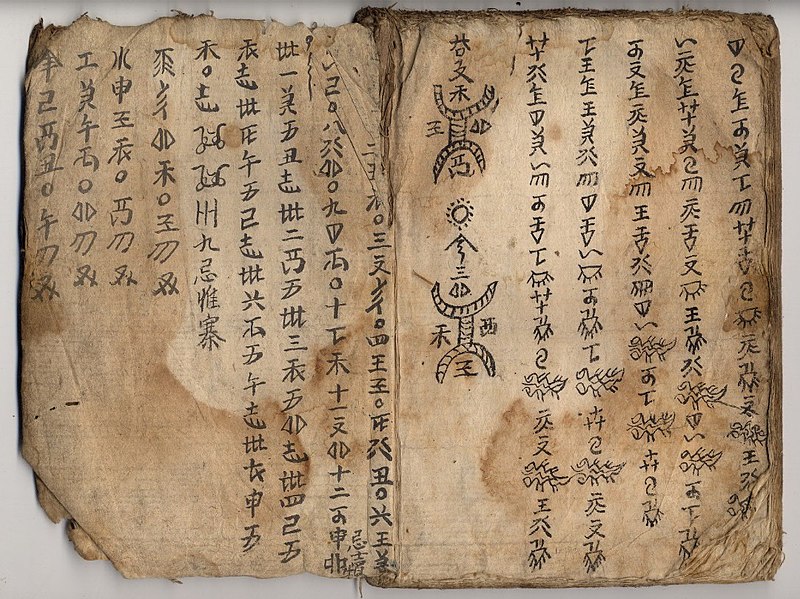
|
| Tangut | Tangut | Northwestern China | 1036–1502 | Han | 
|
| Yi logogram | Nuosu, etc. | Southwestern China | 15th to 16th century – | 
| |
| Zapotec | Zapotec | Mesoamerica | 5th century BC – 8th century | 
|
Han
Han writing system is the one of the logograms that are still used today.
There are 6 ways of creating characters, concluded by scholars in Han dynasty.
It has several different scripts. There used to be many different writings of a characters. After the unification of China, Qin Shi Huang abolished other writings, only keeping Qin State's writing as the official one, written with the small seal script.
During its development, many modifications took place. Wrong characters and unorthodox character variants are plenty. For example, “肉” (flesh) became confused with “月” (moon) and as a result, many characters with meanings related to flesh have the radical 月.
The simplification of Han was also happening through history. For example, “爲” became “為” and finally “为”, like Picasso's bull. In People's Republic of China, there were two attempts of simplification of Han, one of which was successful and the other failed. In Japan, there was one simplification and it was successful.
The writing direction of Han was traditionally top-to-bottom, right-to-left. When writing, the left hand holds the roll of bamboo slips or other materials and the right hand writes. During the modernisation, It has been changed to left-to-right, top-to-bottom.
Currently, it is being used in China and Japan regularly; in Korea and Vietnam sporadically.
There have been some attempts to abolish Han. In China and Japan, they failed; in Korea and Vietnam, they were largely successful. In the Republic of Korea, some people call for having Han along with Hangul in textbooks; In Vietnam, some people call for having Han and Chữ Nôm as a compulsory course in liberal arts.
Related resources:
- Chinese Etymology 字源 https://etymology.azurewebsites.net/ | https://hanziyuan.net/
| script | example |
|---|---|
| oracle bone script | 
|
| bronzeware script | 
|
| seal script | 
(廿六年詔權量銘 Niànliù Nián Zhào Quànliàng Míng) |
| clerical script | 
(華山庙碑 Huà Shān Miào Bēi) |
| regular script | 
(九成宮醴泉銘 Jiǔchéng Gōng Lǐquán Míng) |
| script | example |
|---|---|
| cursive script | 
(書論書 Shūlùn Shū) |
| semicursive script | 
(蘭亭集序 Lántíng Jí Xù) |
Phonogram
Abjad
To avoid the disadvantages of the logogram, this new writing system was formed. In Abjad, the characters represent the consonants.
To show its vowels, there are two ways: add diacritics or become alphabetical.
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ancient South Arabian | Old South Arabian, Ge'ez | South Arabia | 2nd millennium BC – 6th century | Proto-Sinaitic | 
|
| Aramaic | Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, etc. | Mesopotamia | 800 BC – 600 | Phoenician | 
|
| Libyc | Tuareg languages | Sahara and Sahel | first millennium BC – 4th to 7th century | Egyptian? | 
|
| Paleo-Hebrew | Ancient Hebrew | Southern Levant | c. 1000 BC – 135 | Phoenician | 
|
| Phoenician | Phoenician, Punic, etc. | Mediterranea | c. 1050 BC – 150 BC | Proto-Sinaitic | 
|
| Ugaritic | Ugaritic | Ugarit | c. 1400 BC – 1190 BC | 
| |
| Samaritan | Samaritan | Levant | 600 BC – | Paleo-Hebrew | 
|
| Tifinagh | Tuareg languages | Sahara and Sahel | 1980s – | Libyco-Berber | 
|
Phoenician
Phoenician was derived from Egyptian and is the ancestor of most writing systems in the current time.
The writing direction of Phoenician was right-to-left, top-to-bottom. When writing, the left hand presses the parchment or other materials and the right hand writes.
Syllabary
In this type of writing systems, every letter is a syllable.
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afaka | Eastern Maroon Creole | Suriname | 1910 – | 
| |
| Cherokee | Cherokee | Southeastern Woodlands | 1820s – | 
| |
| Kana | Japanese | Japan | c. 800 – | Han | |
| Linear B | Mycenaean Greek | Mycenae | c. 1450 BC – 1200 BC | Linear A | 
|
| Vai | Vai | Liberia | 1830s – | 
| |
| Yi syllabary | Nuosu, etc. | Southwestern China | 1974 – | Yi logogram | 
|
Abugida
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geʽez | Geʽez, Tigrinya, Amharic, etc. | Horn of Africa | c. 1st century – 4th century (as abjad), – (as abugida) | Ancient South Arabian | 
|
| Thaana | Dhivehi | Maldives | 1970s – | Hindu-Arabic numerals | 
|
Alphabet
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adlam | Fulah | Sahel | 1989 – | 
| |
| Greek | Greek | Greece | c. 800 BC – | Phoenician | 
|
Semi-syllabary
In this type of writing system, a letter may be a syllable or a phoneme. It is a combination of syllabary and alphabet.
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bamum | Bamum | Western Cameroon | c. 1896 – | 
| |
| Bopomofo | Chinese | China | 1918 – | Han | 
|
| Celtiberian | Celtiberian | Northeastern Iberia | 5th century BC – ? | Phoenician | 
|
| Northeastern Iberian | Iberian | Northeastern Iberia | 5th century BC – ? | Phoenician | 
|
| Old Persian cuneiform | Old Persian | Persia | 525 BC – 330 BC | 
| |
| Sortheastern Iberian | Iberian | Sortheastern Iberia | 5th century BC – ? | Phoenician | 
|
| Tartessian | Tartessian | Southwest Iberia | 5th century BC – ? | Phoenician | 
|
Featural writing system
This type of writing systems has phonological features. It is based on phonology, so it is the latest type of writing system. They are designed and thus often considered more precise than most other phonograms in use. Its disadvantage is leaving fewer clues on the evolution of the language.
| writing system | language | region | timespan | parent writing system | example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canadian | Algonquian languages, Eskaleut languages, Athabaskan languages | Canada | 1840s – | Devanagari | 
|
| Ditema tsa Dinoko | Southern Bantu languages, Swazi | South Africa | 2010s – | .jpg)
| |
| Duployan shorthand | multiple languages | world | 1868 – | 
| |
| Gregg shorthand | multiple languages | world | 1888 – | 
| |
| Hangul | Korean | Korea | 1443 – | Han | 
|
| Quikscript | English | North America | c. 1966 – | 
| |
| Shavian | English, Esperanto | North America | 1960s – | 
| |
| SignWriting | sign languages | world | 1974 – | 
| |
| Visible Speech | multiple languages | world | 1867 – | 
|
