Difference between revisions of "Language/Dutch/Culture/Education"
m (Quick edit) |
|||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: | [[File:Education system in Dutch.png|alt=Education system in Dutch|thumb|Education system in Dutch]] | ||
'''The Dutch education system is quite unique and different from most countries, which is why I hope that this information gives you a better understanding of our system 😊''' | |||
The education system in the Netherlands is characterized by division, as it caters to the diverse learning needs of different pupils. Education is compulsory in the Netherlands from the age of 5 till 18, although most people start with primary school the day after they turn 4. | |||
A child usually goes through kindergarten ('''peuterspeelzaal'''), primary school '''(basisschool'''), high school ('''middelbare school/voortgezet onderwijs''') and later some form of vocational education ('''mbo''') and/or higher education ('''hoger onderwijs'''). | |||
To further explore Dutch culture and its rich history, you can also check out our pages on [[Language/Dutch/Culture/History-and-Traditions|Dutch history and traditions]], as well as the timelines of two Dutch-speaking countries: [[Language/Dutch/Culture/Sint-Maarten-Timeline|Sint Maarten]] and [[Language/Dutch/Culture/Suriname-Timeline|Suriname]]. Enjoy your journey into the world of Dutch education and culture! 😃 | |||
== '''Basisschool (Primary School)''' == | |||
[[File:300px-Dutch Education System-en.svg.png|thumb|Dutch Education System]]A child attends primary school from the age of 4 until 12, which is divided in eight groups based on age. During the first few years of this school period it is unlikely that a child receives a lot of homework. As in every country it depends on the school type how much homework is given in the later years. For example: a Jenaplan or Rudolf Steiner school has a different approach than a public school. | |||
== | At the end of primary school every kid needs to take a final test. This test gives an indication of the level of the student (which is needed to assess which level of high school the kid will go to). However, this test is an advise, and the teacher will decide which level would be appropriate for the pupil. | ||
== '''Middelbaar Onderwijs (Secondary Education)''' == | |||
Secondary education in the Netherlands compiles both middle school and high school in English countries. The system in the Netherlands makes a division between different needs of learners, based on the "ease of learning" of students. Depending on the level you are in, you will be in high school from 12-16, 12-17 or 12-18. | Secondary education in the Netherlands compiles both middle school and high school in English countries. The system in the Netherlands makes a division between different needs of learners, based on the "ease of learning" of students. Depending on the level you are in, you will be in high school from 12-16, 12-17 or 12-18. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 22: | ||
In all levels, English is a compulsory course that everybody has to take. The same goes for Dutch and Physical Education. | In all levels, English is a compulsory course that everybody has to take. The same goes for Dutch and Physical Education. | ||
== Hoger Onderwijs (Higher Education) == | == '''Beroepsonderwijs of Hoger Onderwijs (Higher Education)''' == | ||
Like the secondary education, the higher education in the Netherlands is divided in three main sections. | Like the secondary education, the higher education in the Netherlands is divided in three main sections. | ||
* MBO: Stands for "middelbaar beroepsonderwijs", ('''vocational education'''), which you can | * MBO: Stands for "middelbaar beroepsonderwijs", ('''vocational education'''), which you can enter from VMBO, or any higher levels. It has a big focus on practical learning in the classroom with hands-on training. After completing can enter the job market, or (depending on the level of MBO) can go to HBO. | ||
* HBO: Stands for "hoger beroepsonderwijs" ('''higher vocational education'''), which you can directly enter from HAVO. It is also known as a "University of Applied Sciences". You can follow practical-based programs that take four years, after which you can choose to go to the job market or do a master. | * HBO: Stands for "hoger beroepsonderwijs" ('''higher vocational education'''), which you can directly enter from HAVO. It is also known as a "University of Applied Sciences". You can follow practical-based programs that take four years, after which you can choose to go to the job market or do a master. | ||
* WO/Universiteit: Stands for "wetenschappelijk onderwijs" ('''scientific education''' or '''university''') and is | * WO/Universiteit: Stands for "wetenschappelijk onderwijs" ('''scientific education''' or '''university''') and is also known as a "Research University". A student can enter university after VWO or after having completed one or more years at HBO. There are 13 universities in the Netherlands which are all ranked in the top 200 of ''Times Higher Education''´s World University Rankings, from which eight can be found in the top 100 universities in the world. A Bachelor's Degree usually takes three years, after which most students proceed to do their Master's. | ||
==Other Lessons== | |||
* [[Language/Dutch/Culture/Netherlands-Timeline|Netherlands Timeline]] | |||
* [[Language/Dutch/Culture/Caribbean-Netherlands-Timeline|Caribbean Netherlands Timeline]] | |||
* [[Language/Dutch/Culture/Sint-Maarten-Timeline|Sint Maarten Timeline]] | |||
<span links></span> | |||
Latest revision as of 13:32, 25 March 2023
The Dutch education system is quite unique and different from most countries, which is why I hope that this information gives you a better understanding of our system 😊
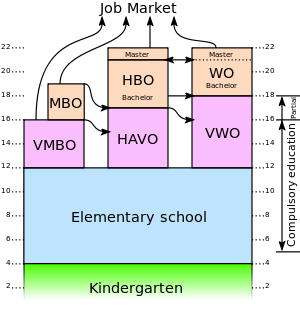
The education system in the Netherlands is characterized by division, as it caters to the diverse learning needs of different pupils. Education is compulsory in the Netherlands from the age of 5 till 18, although most people start with primary school the day after they turn 4.
A child usually goes through kindergarten (peuterspeelzaal), primary school (basisschool), high school (middelbare school/voortgezet onderwijs) and later some form of vocational education (mbo) and/or higher education (hoger onderwijs).
To further explore Dutch culture and its rich history, you can also check out our pages on Dutch history and traditions, as well as the timelines of two Dutch-speaking countries: Sint Maarten and Suriname. Enjoy your journey into the world of Dutch education and culture! 😃
Basisschool (Primary School)[edit | edit source]
A child attends primary school from the age of 4 until 12, which is divided in eight groups based on age. During the first few years of this school period it is unlikely that a child receives a lot of homework. As in every country it depends on the school type how much homework is given in the later years. For example: a Jenaplan or Rudolf Steiner school has a different approach than a public school.
At the end of primary school every kid needs to take a final test. This test gives an indication of the level of the student (which is needed to assess which level of high school the kid will go to). However, this test is an advise, and the teacher will decide which level would be appropriate for the pupil.
Middelbaar Onderwijs (Secondary Education)[edit | edit source]
Secondary education in the Netherlands compiles both middle school and high school in English countries. The system in the Netherlands makes a division between different needs of learners, based on the "ease of learning" of students. Depending on the level you are in, you will be in high school from 12-16, 12-17 or 12-18.
The levels can generally be divided into three sections (some sections have multiple sublevels but that is really going into details)
- VMBO: The abbrevation stands for "voortgezet middelbaar beroepsonderwijs" (pre-vocational secondary education), which is the lowest level of the three and is basically a prep school for vocational secondary Dutch education (middelbaar beroepsonderwijs MBO). It takes 4 years, so from the age of 12-16
- HAVO: The abbrevation stands for "hoger algemeen voortgezet onderwijs" (senior general secondary education), which is the middle level of the three. It takes 5 years, so from the age of 12-17. It provides entrance to higher professional education (hoger beroepsonderwijs HBO) at ‘vocational universities’.
- VWO: The abbrevation stands for "voortgezet wetenschappelijk onderwijs" (scientific secondary education), which is the highest level and will prep you for academic studies at research universities.
In all levels, English is a compulsory course that everybody has to take. The same goes for Dutch and Physical Education.
Beroepsonderwijs of Hoger Onderwijs (Higher Education)[edit | edit source]
Like the secondary education, the higher education in the Netherlands is divided in three main sections.
- MBO: Stands for "middelbaar beroepsonderwijs", (vocational education), which you can enter from VMBO, or any higher levels. It has a big focus on practical learning in the classroom with hands-on training. After completing can enter the job market, or (depending on the level of MBO) can go to HBO.
- HBO: Stands for "hoger beroepsonderwijs" (higher vocational education), which you can directly enter from HAVO. It is also known as a "University of Applied Sciences". You can follow practical-based programs that take four years, after which you can choose to go to the job market or do a master.
- WO/Universiteit: Stands for "wetenschappelijk onderwijs" (scientific education or university) and is also known as a "Research University". A student can enter university after VWO or after having completed one or more years at HBO. There are 13 universities in the Netherlands which are all ranked in the top 200 of Times Higher Education´s World University Rankings, from which eight can be found in the top 100 universities in the world. A Bachelor's Degree usually takes three years, after which most students proceed to do their Master's.
Other Lessons[edit | edit source]