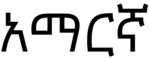Difference between revisions of "Language/Amharic/Grammar/Amharic-Alphabets"
m (Quick edit) |
m (Quick edit) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Amharic-Page-Top}} | {{Amharic-Page-Top}} | ||
<div class="pg_page_title">[[Language/Amharic|Amharic]] → [[Language/Amharic/Grammar|Grammar]] → [[Language/Amharic/Grammar/0-to-A1-Course|0 to A1 Course]] → Basic Amharic Structure → Amharic Alphabets</div> | |||
{{#seo: | |||
|title=Amharic Grammar → Basic Amharic Structure → Amharic Alphabets | |||
|keywords=Amharic, Grammar, Basic Amharic Structure, Amharic Alphabets | |||
|description=Learn the Amharic alphabet and its pronunciation in this comprehensive lesson on Amharic grammar. | |||
}} | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Introduction == | |||
In this lesson, we will explore the basics of Amharic structure, starting with the Amharic alphabet. The Amharic alphabet is an important foundation for learning the Amharic language, as it is the basis for reading, writing, and pronunciation. Understanding the Amharic alphabet will enable you to form words and sentences correctly, and communicate effectively in Amharic. | |||
Throughout this lesson, we will provide detailed explanations, examples, and exercises to help you grasp the Amharic alphabet and its pronunciation. We will also explore any regional variations in the usage or understanding of the alphabet, as well as share interesting cultural facts related to the topic. By the end of this lesson, you will have a solid understanding of the Amharic alphabet and be able to confidently read and write in Amharic. | |||
Let's dive into the fascinating world of the Amharic alphabet! | |||
== The Amharic Alphabet == | |||
The Amharic alphabet, also known as the Ge'ez script, is a writing system used for the Amharic language, which is the official language of Ethiopia. It is derived from the ancient Ge'ez script, which originated in the Aksumite Empire around the 5th century AD. The Amharic alphabet consists of 33 basic characters, each representing a unique sound in the language. | |||
=== Consonants === | |||
The Amharic alphabet consists of 33 consonant characters, which are represented by symbols. These symbols are written from left to right and are grouped into seven series based on their pronunciation. Each series has a distinct sound, and it is important to learn the correct pronunciation of each consonant to accurately read and pronounce Amharic words. | |||
Here is a table | Here is a table of the Amharic consonants, along with their pronunciation and English equivalents: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
! Amharic !! Pronunciation !! English | ! Amharic !! Pronunciation !! English Translation | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ሀ || Ha || H | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ለ || Le || L | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ሐ || Ha || H | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | መ || Me || M | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ሠ || Se || S | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ረ || Re || R | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ሰ || Se || S | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ሸ || She || Sh | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ቀ || Ke || K | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | በ || Be || B | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ተ || Te || T | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ኀ || Ha || H | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ነ || Ne || N | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ኘ || Ne || N | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | አ || A || A | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ከ || Ke || K | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ኸ || Khe || Kh | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ወ || We || W | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ዐ || 'A || ' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ዘ || Ze || Z | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ዠ || Ze || Z | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | የ || Ye || Y | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ደ || De || D | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ዸ || De || D | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ገ || Ge || G | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ጠ || Te || T | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ጰ || Pe || P | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ጸ || Se || S | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ፀ || Se || S | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ፈ || Fe || F | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ፐ || Pe || P | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ፘ || Pe || P | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | ፠ || Fe || F | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== The | === Vowels === | ||
In addition to the consonant characters, the Amharic alphabet also includes a set of vowel characters. Vowels are essential for correct pronunciation and are indicated by diacritical marks placed above or below the consonant characters. There are seven vowel sounds in Amharic, represented by these marks: | |||
- ሀ (Ha) with no diacritic mark represents the "a" sound. | |||
- ለ (Le) with a horizontal line below represents the "e" sound. | |||
- ሐ (Ha) with a dot below represents the "u" sound. | |||
- መ (Me) with a vertical line below represents the "i" sound. | |||
- ሠ (Se) with a dot above represents the "ee" sound. | |||
- ረ (Re) with a dot above represents the "e" sound. | |||
- ሰ (Se) with a horizontal line above represents the "o" sound. | |||
It is important to pay attention to the diacritical marks when reading and pronouncing Amharic words, as they significantly affect the meaning and sound of the word. | |||
=== Syllable Structure === | |||
Amharic words are typically composed of a sequence of consonant-vowel (CV) syllables. Each syllable consists of a consonant followed by a vowel, with the vowel indicating the sound produced by the syllable. The syllable structure is fundamental to understanding the pronunciation and spelling of Amharic words. | |||
For example, let's consider the word "አማርኛ" (Amharic), which means "Amharic" in English. In this word, we can identify four CV syllables: "አ" (a), "ማ" (ma), "ር" (ri), and "ኛ" (gna). By breaking down the word into syllables, we can accurately pronounce it and understand its structure. | |||
=== Cultural Insight === | |||
The Amharic alphabet is not only a tool for communication but also an important aspect of Ethiopian culture. The Ge'ez script, from which the Amharic alphabet is derived, has a rich history dating back to ancient times. It was used to write religious texts, historical accounts, and literature, making it an integral part of Ethiopia's cultural heritage. | |||
The Amharic alphabet is also closely tied to the Ethiopian Orthodox Church, which has played a significant role in Ethiopian history and society. The Church uses the Amharic language for its liturgy, and the alphabet is taught in religious schools. Understanding the Amharic alphabet allows individuals to engage more deeply with the cultural and religious aspects of Ethiopian society. | |||
== Exercises == | |||
Now that we have covered the basics of the Amharic alphabet, let's practice what we have learned through some exercises. | |||
Exercise 1: Write the following Amharic words in English translation: | |||
1. ለጥፋት | |||
2. ተሰማ | |||
3. አትሌት | |||
4. አስጸያፊ | |||
5. በረከት | |||
Exercise 2: Write the following English words in Amharic: | |||
1. Language | |||
2. Culture | |||
3. Book | |||
4. Music | |||
5. Coffee | |||
Exercise 3: Match the Amharic consonant with its correct pronunciation: | |||
1. ሀ | |||
2. ለ | |||
3. ሰ | |||
4. ከ | |||
5. የ | |||
A. R | |||
B. L | |||
C. H | |||
D. S | |||
E. Y | |||
== Solutions == | |||
Exercise 1: | |||
1. Letfāt - Meaning: "beauty" | |||
2. Tesama - Meaning: "peace" | |||
3. Atlet - Meaning: "athlete" | |||
4. Asṭāyafi - Meaning: "photographer" | |||
5. Bereket - Meaning: "blessing" | |||
Exercise 2: | |||
1. ቋንቋ (Kañña) - Meaning: "language" | |||
2. ባህላዊ (Bahilawi) - Meaning: "cultural" | |||
3. መጽሐፍ (Meṣḥaf) - Meaning: "book" | |||
4. ሙዚቃ (Muziqa) - Meaning: "music" | |||
5. ቡና (Buna) - Meaning: "coffee" | |||
Exercise 3: | |||
1. C (ሀ) - Pronunciation: "Ha" | |||
2. B (ለ) - Pronunciation: "Le" | |||
3. D (ሰ) - Pronunciation: "Se" | |||
4. K (ከ) - Pronunciation: "Ke" | |||
5. Z (የ) - Pronunciation: "Ye" | |||
== Conclusion == | == Conclusion == | ||
In | In this lesson, we explored the Amharic alphabet and its pronunciation. We learned about the consonant and vowel characters, as well as the syllable structure of Amharic words. By understanding the Amharic alphabet, you now have the foundation to read, write, and pronounce Amharic words accurately. | ||
The Amharic alphabet is not only a practical tool for communication but also an integral part of Ethiopian culture. It is deeply connected to the country's history, religion, and literature. By learning the Amharic alphabet, you are immersing yourself in the rich cultural heritage of Ethiopia. | |||
Keep practicing the Amharic alphabet, and in the next lesson, we will explore pronouns and greetings in Amharic. Good luck! | |||
{{Amharic-0-to-A1-Course-TOC}} | |||
[[Category:Course]] | |||
[[Category:Amharic-Course]] | |||
[[Category:0-to-A1-Course]] | |||
[[Category:Amharic-0-to-A1-Course]] | |||
<span gpt></span> <span model=gpt-3.5-turbo-16k></span> <span temperature=0.7></span> | |||
==Sources== | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amharic Amharic - Wikipedia] | |||
* [https://www.ethiopianlegacy.com/courses/amharic-global-live-virtual-course Amharic Global Live Virtual Course] | |||
* [https://staging.jhcenterforthearts.org/viewcontent?dataid=58685&FileName=Basic%20Amharic%20A%20Teaching%20Amharic%20Edition.pdf Basic Amharic A Teaching Amharic Edition (Download Only ...] | |||
==Other Lessons== | ==Other Lessons== | ||
| Line 143: | Line 220: | ||
* [[Language/Amharic/Grammar/Basic-Prepositions-and-Adverbs|Basic Prepositions and Adverbs]] | * [[Language/Amharic/Grammar/Basic-Prepositions-and-Adverbs|Basic Prepositions and Adverbs]] | ||
{{Amharic-Page-Bottom}} | {{Amharic-Page-Bottom}} | ||
Revision as of 09:17, 21 June 2023
Introduction
In this lesson, we will explore the basics of Amharic structure, starting with the Amharic alphabet. The Amharic alphabet is an important foundation for learning the Amharic language, as it is the basis for reading, writing, and pronunciation. Understanding the Amharic alphabet will enable you to form words and sentences correctly, and communicate effectively in Amharic.
Throughout this lesson, we will provide detailed explanations, examples, and exercises to help you grasp the Amharic alphabet and its pronunciation. We will also explore any regional variations in the usage or understanding of the alphabet, as well as share interesting cultural facts related to the topic. By the end of this lesson, you will have a solid understanding of the Amharic alphabet and be able to confidently read and write in Amharic.
Let's dive into the fascinating world of the Amharic alphabet!
The Amharic Alphabet
The Amharic alphabet, also known as the Ge'ez script, is a writing system used for the Amharic language, which is the official language of Ethiopia. It is derived from the ancient Ge'ez script, which originated in the Aksumite Empire around the 5th century AD. The Amharic alphabet consists of 33 basic characters, each representing a unique sound in the language.
Consonants
The Amharic alphabet consists of 33 consonant characters, which are represented by symbols. These symbols are written from left to right and are grouped into seven series based on their pronunciation. Each series has a distinct sound, and it is important to learn the correct pronunciation of each consonant to accurately read and pronounce Amharic words.
Here is a table of the Amharic consonants, along with their pronunciation and English equivalents:
| Amharic | Pronunciation | English Translation |
|---|---|---|
| ሀ | Ha | H |
| ለ | Le | L |
| ሐ | Ha | H |
| መ | Me | M |
| ሠ | Se | S |
| ረ | Re | R |
| ሰ | Se | S |
| ሸ | She | Sh |
| ቀ | Ke | K |
| በ | Be | B |
| ተ | Te | T |
| ኀ | Ha | H |
| ነ | Ne | N |
| ኘ | Ne | N |
| አ | A | A |
| ከ | Ke | K |
| ኸ | Khe | Kh |
| ወ | We | W |
| ዐ | 'A | ' |
| ዘ | Ze | Z |
| ዠ | Ze | Z |
| የ | Ye | Y |
| ደ | De | D |
| ዸ | De | D |
| ገ | Ge | G |
| ጠ | Te | T |
| ጰ | Pe | P |
| ጸ | Se | S |
| ፀ | Se | S |
| ፈ | Fe | F |
| ፐ | Pe | P |
| ፘ | Pe | P |
| ፠ | Fe | F |
Vowels
In addition to the consonant characters, the Amharic alphabet also includes a set of vowel characters. Vowels are essential for correct pronunciation and are indicated by diacritical marks placed above or below the consonant characters. There are seven vowel sounds in Amharic, represented by these marks:
- ሀ (Ha) with no diacritic mark represents the "a" sound. - ለ (Le) with a horizontal line below represents the "e" sound. - ሐ (Ha) with a dot below represents the "u" sound. - መ (Me) with a vertical line below represents the "i" sound. - ሠ (Se) with a dot above represents the "ee" sound. - ረ (Re) with a dot above represents the "e" sound. - ሰ (Se) with a horizontal line above represents the "o" sound.
It is important to pay attention to the diacritical marks when reading and pronouncing Amharic words, as they significantly affect the meaning and sound of the word.
Syllable Structure
Amharic words are typically composed of a sequence of consonant-vowel (CV) syllables. Each syllable consists of a consonant followed by a vowel, with the vowel indicating the sound produced by the syllable. The syllable structure is fundamental to understanding the pronunciation and spelling of Amharic words.
For example, let's consider the word "አማርኛ" (Amharic), which means "Amharic" in English. In this word, we can identify four CV syllables: "አ" (a), "ማ" (ma), "ር" (ri), and "ኛ" (gna). By breaking down the word into syllables, we can accurately pronounce it and understand its structure.
Cultural Insight
The Amharic alphabet is not only a tool for communication but also an important aspect of Ethiopian culture. The Ge'ez script, from which the Amharic alphabet is derived, has a rich history dating back to ancient times. It was used to write religious texts, historical accounts, and literature, making it an integral part of Ethiopia's cultural heritage.
The Amharic alphabet is also closely tied to the Ethiopian Orthodox Church, which has played a significant role in Ethiopian history and society. The Church uses the Amharic language for its liturgy, and the alphabet is taught in religious schools. Understanding the Amharic alphabet allows individuals to engage more deeply with the cultural and religious aspects of Ethiopian society.
Exercises
Now that we have covered the basics of the Amharic alphabet, let's practice what we have learned through some exercises.
Exercise 1: Write the following Amharic words in English translation:
1. ለጥፋት 2. ተሰማ 3. አትሌት 4. አስጸያፊ 5. በረከት
Exercise 2: Write the following English words in Amharic:
1. Language 2. Culture 3. Book 4. Music 5. Coffee
Exercise 3: Match the Amharic consonant with its correct pronunciation:
1. ሀ 2. ለ 3. ሰ 4. ከ 5. የ
A. R B. L C. H D. S E. Y
Solutions
Exercise 1: 1. Letfāt - Meaning: "beauty" 2. Tesama - Meaning: "peace" 3. Atlet - Meaning: "athlete" 4. Asṭāyafi - Meaning: "photographer" 5. Bereket - Meaning: "blessing"
Exercise 2: 1. ቋንቋ (Kañña) - Meaning: "language" 2. ባህላዊ (Bahilawi) - Meaning: "cultural" 3. መጽሐፍ (Meṣḥaf) - Meaning: "book" 4. ሙዚቃ (Muziqa) - Meaning: "music" 5. ቡና (Buna) - Meaning: "coffee"
Exercise 3: 1. C (ሀ) - Pronunciation: "Ha" 2. B (ለ) - Pronunciation: "Le" 3. D (ሰ) - Pronunciation: "Se" 4. K (ከ) - Pronunciation: "Ke" 5. Z (የ) - Pronunciation: "Ye"
Conclusion
In this lesson, we explored the Amharic alphabet and its pronunciation. We learned about the consonant and vowel characters, as well as the syllable structure of Amharic words. By understanding the Amharic alphabet, you now have the foundation to read, write, and pronounce Amharic words accurately.
The Amharic alphabet is not only a practical tool for communication but also an integral part of Ethiopian culture. It is deeply connected to the country's history, religion, and literature. By learning the Amharic alphabet, you are immersing yourself in the rich cultural heritage of Ethiopia.
Keep practicing the Amharic alphabet, and in the next lesson, we will explore pronouns and greetings in Amharic. Good luck!
Sources
- Amharic - Wikipedia
- Amharic Global Live Virtual Course
- Basic Amharic A Teaching Amharic Edition (Download Only ...
Other Lessons
- Using the Conditional
- Asking If and Saying Whether It Is “Suitable” or Not
- “to be” and “to have”
- Expressing Obligation or Necessity
- The Possessive Adjectives
- Complex Sentence
- How to Use Have
- Using the Subjunctive
- Basic Prepositions and Adverbs