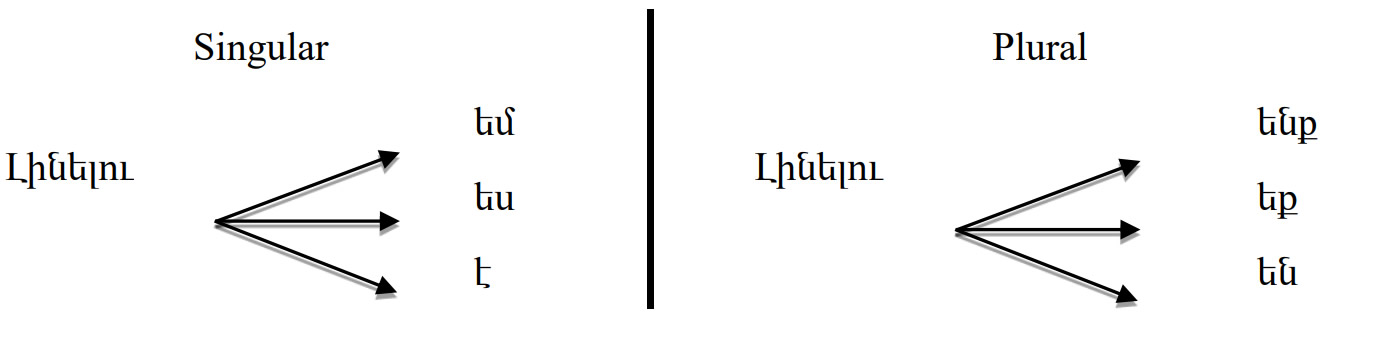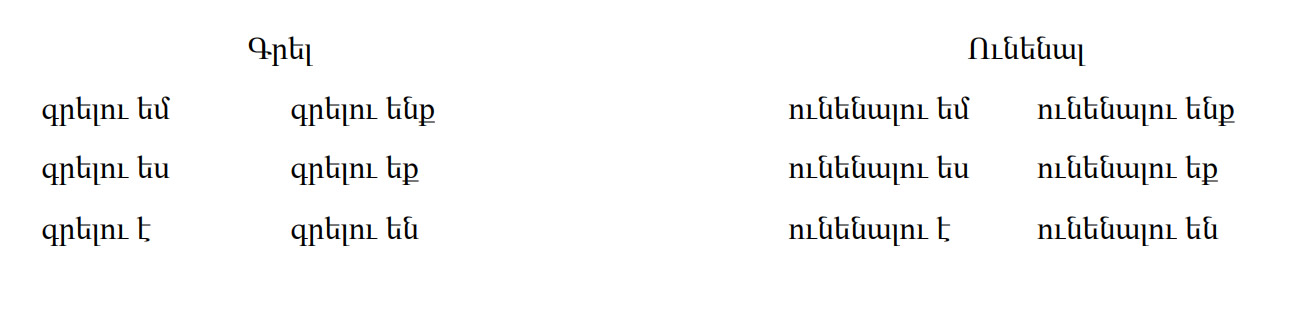Difference between revisions of "Language/Armenian/Grammar/Future-Indicative-Tense"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "thumb <div style="font-size:300%> Future Indicative Tense in Armenian</div> The future tense is formed by adding the ending “ո...") |
m (Quick edit) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
The future tense is formed by adding the ending “ու” to the infinitive form of the verb. This future formation can best be translated by “going to” structure in English. But in many cases it can be translated by “will” modal verb. In the future tense the verb to be becomes: | The future tense is formed by adding the ending “ու” to the infinitive form of the verb. This future formation can best be translated by “going to” structure in English. But in many cases it can be translated by “will” modal verb. In the future tense the verb to be becomes: | ||
[[File:Armenian-Language- Future Indicative Tense PolyglotClub.jpg]] | |||
* Զբոսաշրջիկները լինելու են Ղափանում: The tourists are going to be in Kapan. | |||
All other verbs, both with “ալ” and “ել” ending follow the same pattern. For example, | All other verbs, both with “ալ” and “ել” ending follow the same pattern. For example, | ||
[[File:Armenian-Language- Future Indicative Tense 2 PolyglotClub.jpg]] | |||
# Տաս տարի հետո հայերն ունենալու են հարուստ պետություն: Armenians are going to have a rich state after ten years. | |||
# Վարորդն իր մեքենան նորոգելու է շաբաթ օրը։ The driver is going to fix his car on Saturday. | |||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
https://slaviccenters.duke.edu/sites/slaviccenters.duke.edu/files/handbook_of_armenian.pdf | https://slaviccenters.duke.edu/sites/slaviccenters.duke.edu/files/handbook_of_armenian.pdf | ||
==Other Lessons== | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/present-simple-and-present-continuous|present simple and present continuous]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/The-Nominative-Case|The Nominative Case]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/Indefinite-Pronouns|Indefinite Pronouns]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/Adjectives|Adjectives]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/Demonstrative-pronouns|Demonstrative pronouns]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/Imperative-Mood|Imperative Mood]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/The-Past-Perfect-Tense|The Past Perfect Tense]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/Verb-Declension|Verb Declension]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/Simple-Past|Simple Past]] | |||
* [[Language/Armenian/Grammar/The-Definite-Article|The Definite Article]] | |||
<span links></span> | |||
Latest revision as of 13:12, 27 March 2023
Future Indicative Tense in Armenian
The future tense is formed by adding the ending “ու” to the infinitive form of the verb. This future formation can best be translated by “going to” structure in English. But in many cases it can be translated by “will” modal verb. In the future tense the verb to be becomes:
- Զբոսաշրջիկները լինելու են Ղափանում: The tourists are going to be in Kapan.
All other verbs, both with “ալ” and “ել” ending follow the same pattern. For example,
- Տաս տարի հետո հայերն ունենալու են հարուստ պետություն: Armenians are going to have a rich state after ten years.
- Վարորդն իր մեքենան նորոգելու է շաբաթ օրը։ The driver is going to fix his car on Saturday.
Sources[edit | edit source]
https://slaviccenters.duke.edu/sites/slaviccenters.duke.edu/files/handbook_of_armenian.pdf
Other Lessons[edit | edit source]
- present simple and present continuous
- The Nominative Case
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Adjectives
- Demonstrative pronouns
- Imperative Mood
- The Past Perfect Tense
- Verb Declension
- Simple Past
- The Definite Article