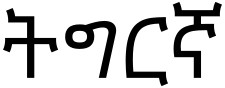Difference between revisions of "Language/Tigrinya/Culture/Geography-of-Eritrea-and-Ethiopia"
m (Quick edit) |
m (Quick edit) |
||
| Line 87: | Line 87: | ||
* [[Language/Tigrinya/Culture/Traditional-Clothing|Traditional Clothing]] | * [[Language/Tigrinya/Culture/Traditional-Clothing|Traditional Clothing]] | ||
* [[Language/Tigrinya/Culture/Eritrea-Timeline|Eritrea Timeline]] | * [[Language/Tigrinya/Culture/Eritrea-Timeline|Eritrea Timeline]] | ||
<span class='maj'></span> | |||
==Sources== | |||
* [https://www.encyclopedia.com/places/africa/eritrea-political-geography/tigrinya Tigrinya | Encyclopedia.com] | |||
{{Tigrinya-Page-Bottom}} | {{Tigrinya-Page-Bottom}} | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 2 April 2023
Introduction
In this lesson, you will learn about the geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia, two neighboring countries that are home to the Tigrinya people. You will discover the major cities, regions, and natural features of these countries while also gaining insight into the cultural significance of their geography. By the end of this lesson, you will have a better understanding of the Tigrinya-speaking regions and the unique features that make them special.
Eritrea
Eritrea is a small country located in northeast Africa, bordered by Sudan to the west and Ethiopia to the south and east. It has a coastline on the Red Sea to the east, which provides important access to global trade routes. Eritrea's geography is characterized by rugged highlands and coastal plains, as well as a number of small islands scattered along the coast.
Major Cities
Eritrea has several major cities that serve as economic and cultural centers. The capital city, Asmara, is located in the central highlands and is known for its well-preserved Italian colonial architecture. Massawa, located on the coast, is a major seaport and has a rich history as a hub of trade and commerce. Keren, in the north, is a regional center for livestock production and has a large market that attracts people from around the region.
Regions
Eritrea is divided into six regions, each with its own unique geography, culture, and history. These regions are:
- Anseba
- Debub (Southern)
- Gash-Barka
- Maakel (Central)
- Northern Red Sea
- Southern Red Sea
Each region has its own capital city and distinct character. For example, Debub is known for its sweeping landscapes and rugged terrain, while the Northern Red Sea region is known for its coral reefs and tourist beaches.
Natural Features
Eritrea has a number of unique natural features that contribute to its biodiversity and scenic beauty. The country's highest peak is Mount Soira, which rises to an elevation of 3,018 meters (9,902 feet) in the center of the country. The Danakil Depression, in the northeastern part of the country, is one of the lowest points on the planet, with parts of the region lying more than 100 meters (328 feet) below sea level. The Gash River, which flows westward from Eritrea into Sudan, provides critical water resources to both countries.
Ethiopia
Ethiopia is a large country located in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, and South Sudan and Sudan to the west. It has a diverse geography characterized by highlands, lowlands, and deserts.
Major Cities
Ethiopia has several major cities, each with its own unique history and character. The capital city, Addis Ababa, is located in the central highlands and is the largest city in the country. It serves as the political and economic center of the country and is home to the African Union headquarters. Dire Dawa, located in the east, is a major commercial center and transportation hub, while Bahir Dar, situated on the shore of Lake Tana in the north, is known for its natural beauty and historic monasteries.
Regions
Ethiopia is divided into ten regions, each with its own distinct geography, culture, and history. These regions are:
- Afar
- Amhara
- Benishangul-Gumuz
- Dire Dawa
- Gambela
- Harari
- Oromia
- Somali
- Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region (SNNPR)
- Tigray
Each region has its own capital city and unique characteristics. For example, the Amhara region is known for its historic rock-hewn churches, while the Gambela region is characterized by its tropical forests and diverse wildlife.
Natural Features
Ethiopia has a wealth of natural features that contribute to its ecological diversity and scenic beauty. The country's highest peak is Ras Dashen, located in the Semien Mountains, which rises to an elevation of 4,550 meters (14,928 feet). The Danakil Depression, which also extends into Eritrea, is one of the hottest and driest places on the planet, with temperatures that regularly exceed 50 degrees Celsius (122 degrees Fahrenheit). Ethiopia is also home to the Blue Nile, one of the two major tributaries of the Nile River, which originates in the highlands of Ethiopia and contributes significantly to the country's agricultural productivity.
Conclusion
In this lesson, you have learned about the geography of Eritrea and Ethiopia, two neighboring countries that are home to the Tigrinya people. You have discovered the major cities, regions, and natural features of these countries and gained insight into the cultural significance of their geography. By understanding the unique characteristics of the Tigrinya-speaking regions, you have gained a deeper appreciation for the history and culture of these fascinating countries.
Other Lessons
Sources