Difference between revisions of "Language/Northern-uzbek/Grammar/Present-Perfect-Tense"
< Language | Northern-uzbek | Grammar
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*tekkanlar / tekkan - They have touched | *tekkanlar / tekkan - They have touched | ||
==Interrogative form == | |||
Note, that in interrogative sentences for subjects men and biz the suffix –mi is added after personal endings. | |||
[[File:Uzbek-Present-Perfect-Tense-Interrogative-Form-PolyglotClub.jpg]] | |||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
https://slaviccenters.duke.edu/sites/slaviccenters.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/uzbek.original.pdf | https://slaviccenters.duke.edu/sites/slaviccenters.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/uzbek.original.pdf | ||
Revision as of 11:32, 15 September 2021
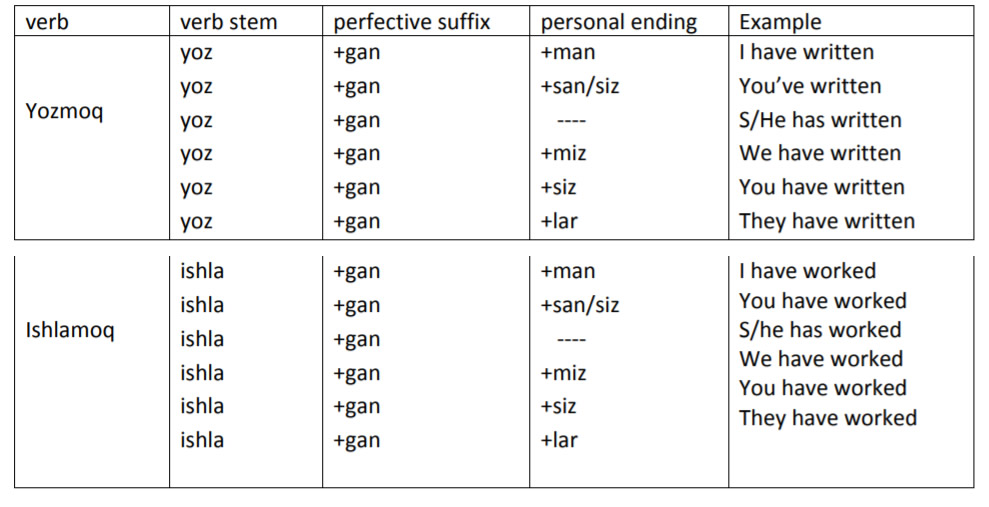
Present Perfect Tense. Tugallangan hozirgi zamon
V + gan + personal ending
This form is used to express action happened in the indefinite past with no specific time frame or dates. It is formed by adding to the verb stem the suffix -GAN, plus the pronominal type of personal suffixes.
For example:
- Men xat yozganman.
- U o’zbek tilini o’rgangan.
- Biz Samarqandda ishlaganmiz.
- Eshikni ochgan bola kim?
If the verb stem ends with -k or -g, a phonetic assimilation rule changes the suffix into -KAN. In the same way, if the verb stem ends with -q or -g', the suffix is changed into -QAN. For example, with the verb tegmoq, 'to touch':
- tekkanman - I have touched
- tekkansan - You have touched
- tekkan - He/she/it has touched
- tekkanmiz - We have touched
- tekkansiz - You have touched
- tekkanlar / tekkan - They have touched
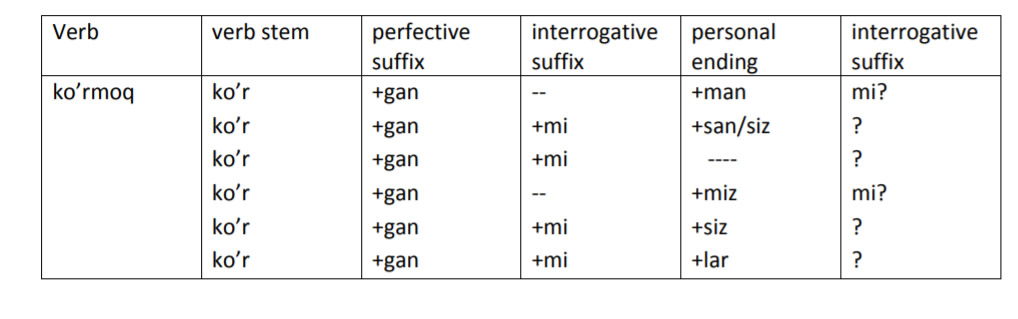
Interrogative form
Note, that in interrogative sentences for subjects men and biz the suffix –mi is added after personal endings.